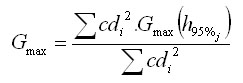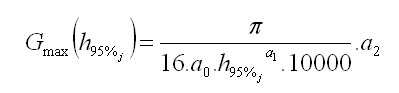This model is based on the logistic regression, which is a function of survival probability (function F-logit):
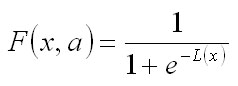
where L(x) is the logical value calculated for a particular tree:
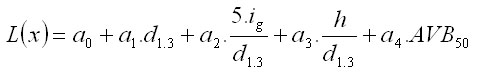
The logical value depends on the tree diameter d1.3, the annual increment of tree basal area ig, the tree height h, and the absolute height (site) class AVB50. Absolute height (site) class is expressed as a potential top height in the simulation plot reached at the age of t = 50 years:
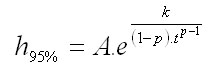
where the coefficients A, k, p are derived from the ecological site classification.
The function of tree survival probability is then transformed to the function of tree mortality (in %) as follows:
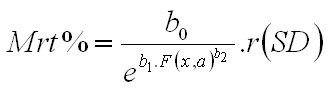
where r(SD) is the value dependent on stand density (SD) determined by SDI according to Reineke (1933). If stand density is greater than or equal to 0.7 (0.8 for pine), r(SD) is equal to 1, otherwise it is equal to SD.
The obtained value Mrt% is then compared with the random number drawn from uniform distribution from the interval <0;100). The tree i dies if the calculated value exceeds the random number:
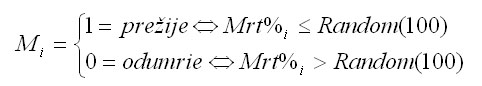
The age at which the tree dies is randomly generated from the 5-year interval. All coefficients are published in Fabrika (2005).